Taking action in the public interest
In creating this Foundation, the Fayat family wanted to make a contribution to solving some of the challenges facing our society. Three areas were particularly important to him: health, education and heritage.
Heritage
Portico artworks, Letarouilly courtyard – Collège de France, Paris 2026–2027
The Foundation supports the preservation of the Collège de France's heritage by funding the restoration of the artworks in the Letarouilly courtyard portico, listed as a Historic Monument. Built between 1834 and 1841, this open-air portico connects teaching spaces and facilitates the movement of visitors between lecture halls and classrooms.
The Letarouilly portico artworks: A living treasure at the Collège de France.
In 2026–2027, the painted decorations of the Letarouilly portico, an architectural masterpiece of the Collège de France, will be the focus of a heritage enhancement campaign. Located at the crossroads of lecture halls and classrooms, they accompany the daily passage of hundreds of visitors.
Executed in a "Pompeian" style by Urbain Bourgeois and Louis Alfred Joseph Hista, the artwork now shows the marks of time—dirt, dust, and faded pigments threaten its legibility. Restoration is essential.
A postdoctoral researcher will study the artwork and its historical context. His or her research, along with the story of the restoration, will be published by the Collège de France.
Founded in 1530, the Collège de France has embodied scientific excellence and intellectual openness for five centuries. Its 50,000 m² of laboratories, 11 lecture halls, and libraries welcome over 100,000 attendees each year for free, open-access courses.
Once restored and illuminated, the portico's artworks will remind us that this place of learning is also a living heritage, serving knowledge and culture.

Health
4th Clément Fayat scholarship : NEUROFEMZEN
Medical research thesis 2025-2028
The work of this thesis aims to evaluate the effectiveness of two non-drug interventions focused on the face — myofascial massage and audio-guided relaxation. The goal is to demonstrate the reduction of chronic stress in women at risk of neurocognitive decline and the ability to restore cerebral, physiological, and emotional balance. This project aligns with the World Health Organization recommendations advocating targeted prevention strategies for women's mental and cognitive health.
Chronic stress profoundly affects mental, emotional, and physical health, particularly in women. It causes fatigue, sleep disturbances, attention and memory difficulties, irritability, and emotional dysregulation. It also increases vulnerability to anxiety and depressive disorders and is a major risk factor in the onset of neurodegenerative diseases.
In this context, targeted, non-drug prevention strategies are essential to reduce the impact of stress, support daily well-being, and protect brain health. Moreover, chronic stress does not manifest uniformly: its intensity, frequency, somatic, emotional, or cognitive expressions, as well as sensitivity to hormonal fluctuations—especially during the peri- and post-menopausal transition—vary greatly from one woman to another. Offering tailored approaches, adjusted to stress profiles and individual needs, is therefore crucial to optimise intervention effectiveness.
The NEUROFEMZEN project fully aligns with the recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO) which advocates the development of complementary interventions that are accessible, free of side effects, and specifically adapted to women's needs. It also reflects a broader trend toward personalised interventions, a major challenge in women's health.
Studying two distinct body-based approaches—facial myofascial massage, based on therapeutic touch, and audio-guided relaxation, which uses focused listening to induce deep bodily relaxation—offers a flexible method capable of adapting to individual preferences and the dominant type of stress (physiological, emotional, or cognitive). This project paves the way for truly personalised, prevention-oriented protocols.
Building on promising preliminary results, this research aims to establish the scientific foundations necessary for integrating these body-based practices into supportive care in neurology. The protocol will assess the impact of facial myofascial massage and guided relaxation on perceived stress, as well as on a comprehensive set of mental, emotional, and brain health indicators: well-being, quality of life, sleep, self-esteem, body awareness, vagal tone, and brain activity measured by MRI.
The originality of the project lies in highlighting the face as a therapeutic body–mind interface, opening new clinical perspectives for women exposed to significant stress, particularly those aged 40 to 60—a period of hormonal transition marked by increased endocrine and brain vulnerability.
This thesis work is conducted within the team of Laure Zago, a CNRS researcher at the Institute of Neurodegenerative Diseases (IMN) at Bordeaux Neurocampus.

Health
CbgMotDisorders Project 2025-2027 Research Grant
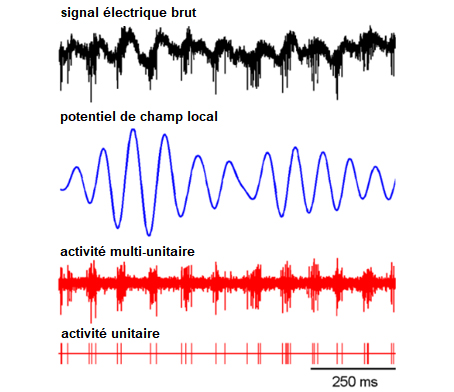
This project aims to characterized Parkinsonian neuronal electrical oscillations in the brain of primates and establish a link with motor deficits of Parkinson's disease. The goal is to develop innovative treatments to restore movement in patients with Parkinson's disease.
In Parkinson's disease, involuntary or jerky movements (Dyskinesia) and slow delayed movements difficult to initiate (Akinisia) are accompanied by abnormal oscillatory electrical activities in the brain. The involvement of these neuronal oscillations in the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease remains to be clarified. Changes in frequency and synchronization of these neuronal oscillations could lead to motor deficits.
Identifying the properties of neuronal oscillations in the different brain structures involved in normal and pathological motor control (Parkinsonian state) will provide major results to advance and propose innovative therapies to restore movement in Parkinsonian patients.
This multidisciplinary project is led by Marc DEFFAINS, CNRS Researcher of the Procedural Learning Network Dynamics team at the Broca Centre of the University of Bordeaux, and Dominique GUELH, PU-PH, of the Clinical Neurophysiology Department of the Broca Centre of the University of Bordeaux.
Health
TPE MODULE Project 2024-2026 Therapeutic Education programme
The project at Les Pyrénées Hospital in Pau (Pyrénées-Atlantiques) involves the creation of innovative tools to meet the educational objectives of a therapeutic education (TPE) module designed for carers of patients suffering from a recently diagnosed neurodegenerative disorder.
The programme will also include educational sessions for patients.
The Transversal Psychiatric Therapeutic Patient Education Unit at Les Pyrénées Hospital in Pau (Pyrénées-Atlantiques), in collaboration with the geriatric psychiatry team and France Alzheimer des Pyrénées Atlantique (FAPA), is developing a TPE module aimed at carers of loved ones suffering from neurodegenerative diseases. Funding from the Foundation is helping to develop:
- 3D models to improve the ergonomics of the patient's environment and independence without them losing their bearings;
- videos to promote communication.
To ensure that carers are available to attend these sessions without feeling guilty about leaving their loved one alone, educational and cognitive remediation sessions are planned at the same time as the TPE sessions.
The aim is also to expand the multi-disciplinary team of facilitators by training them in TPE facilitation, to enable the dissemination of the module throughout the Béarn Soule region.
Health
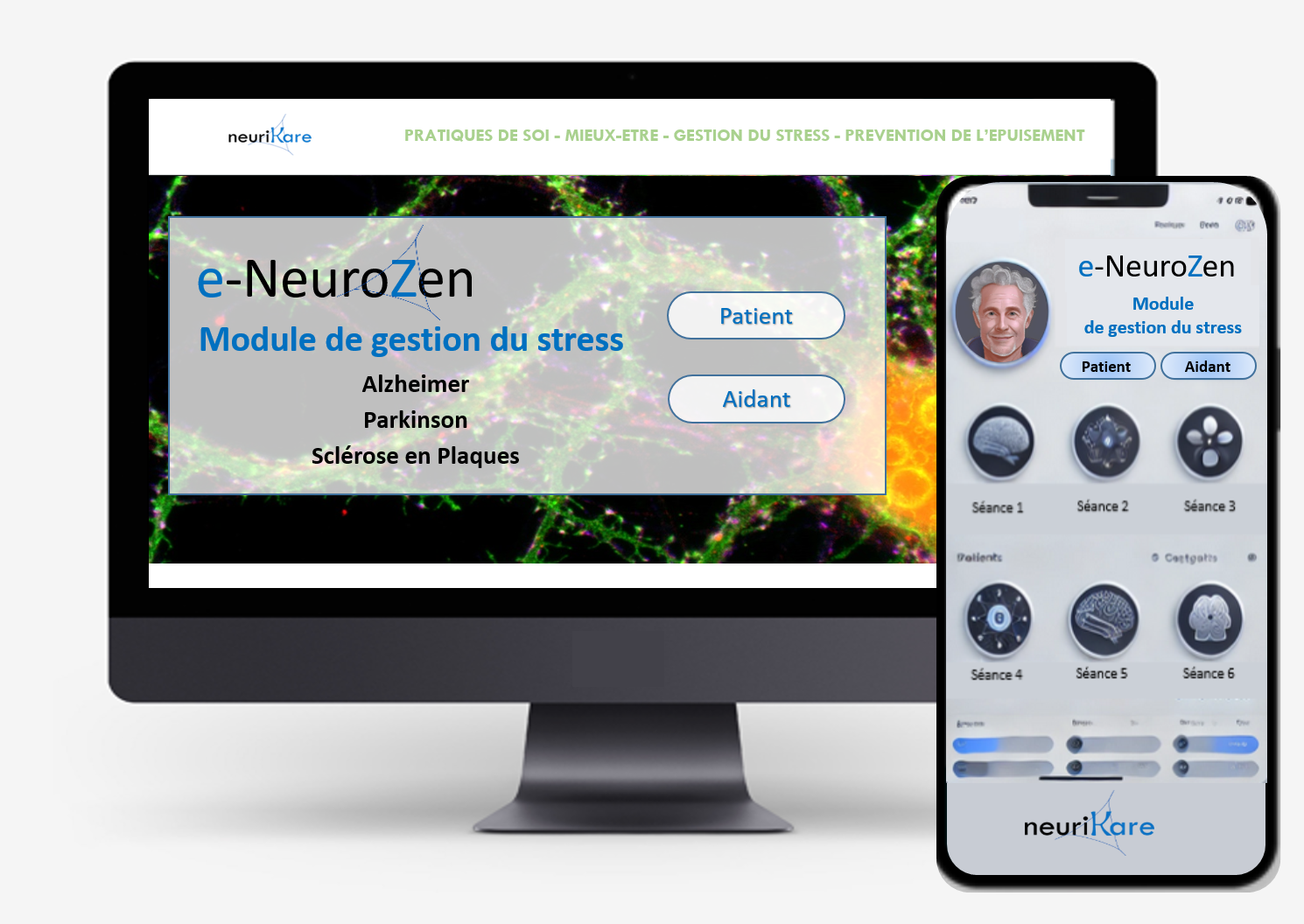
e-NeuroZen project 2024-2026 Therapeutic Education programme
This project aims to develop a digital platform with modules on the acquisition of stress-management skills. The modules will support existing therapeutic education (TPE) programmes at Bordeaux University Hospital. Aimed at carers and patients suffering from neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's, early-onset Alzheimer's and multiple sclerosis, this digital platform will facilitate access for as many people as possible.
A survey conducted by Odoxa in May 2023 revealed that half of the French population would be willing to use complementary non-drug therapies. These practices are often proposed by regional “neurodegenerative disease” centres of expertise as part of therapeutic patient education (TPE) programmes for Parkinson's, early-onset Alzheimer's and multiple sclerosis. Examples include practices originating in the USA and based on the mind-body connection, which are attracting growing interest in the field of neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs). A growing body of evidence points towards the relative effectiveness of such interventions in structured stress-management programmes based on mindfulness. These structured programmes are incorporated into TPE programmes designed to improve self-care and coping skills (lifestyle, self-knowledge, self-esteem, emotional regulation, interpersonal and communication skills, etc.).
Mindfulness meditation has only recently been incorporated into TPE in France.
This multi-disciplinary project is led by François Tison, a university professor and practising neurologist, in the framework of the NeuriKare commission of the Maison du Cerveau association (Bordeaux).
Health
TOPAZ project 2024 – 2025 Complementary non-pharmacological intervention
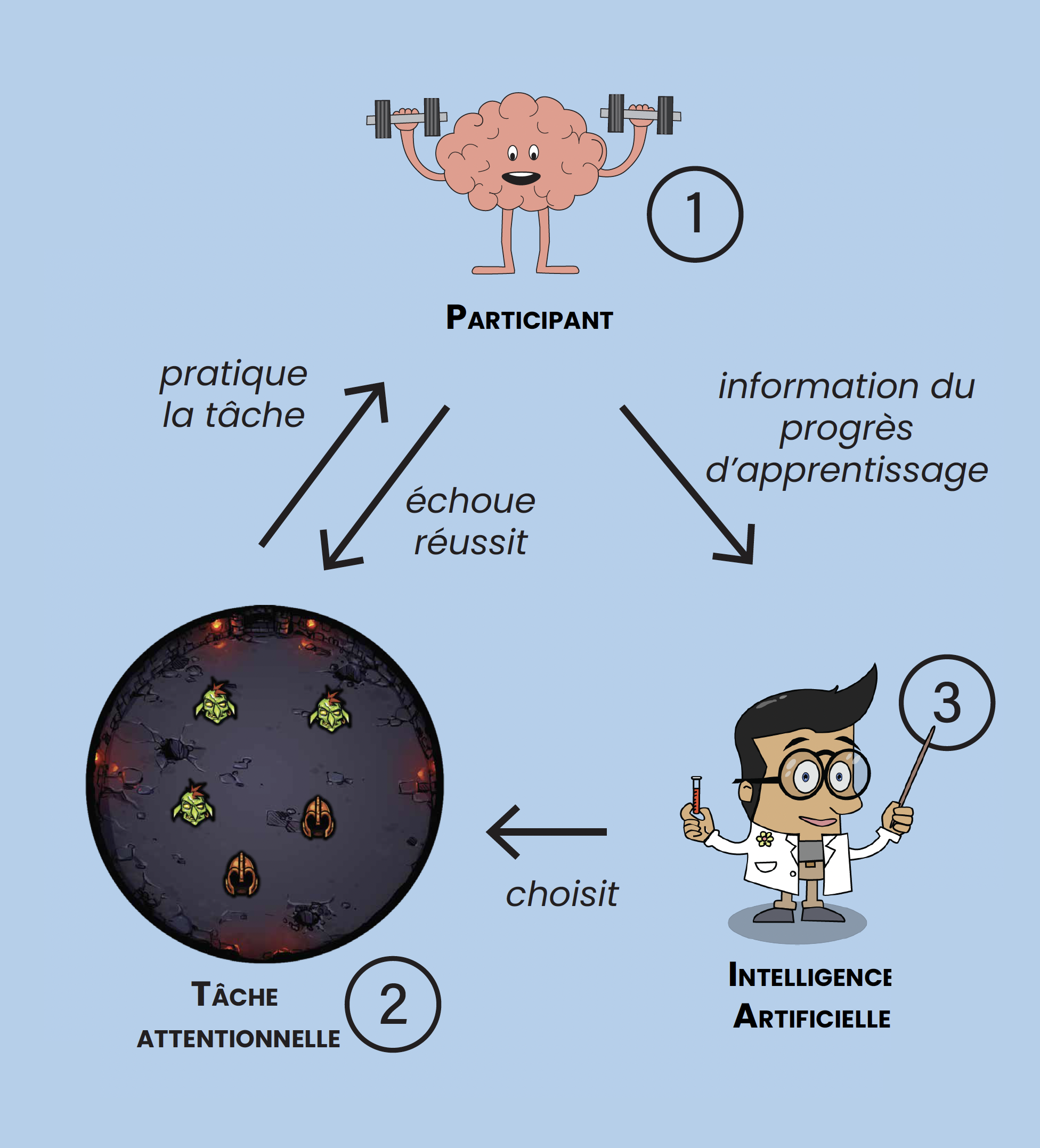
Attention is an indicator of good cognitive health and a clinical marker of the early stages of vascular dementia. Computerised attention span training demonstrates significant improvements but with high interindividual variability. With the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the project aims to show in elderly people or people with early-stage vascular dementia that customised training makes computerised attention training effective for all.
This project is coordinated by the FLOWERS team featuring the University of Bordeaux INRIA Centre (French National Institute for Research in Digital Science and Technology) and PARISTECH’s ENSTA multidisciplinary engineering school, headed up by Marion PECH, PhD. Postdoctoral student.
This interdisciplinary project combines both AI skills and clinical skills, providing cognitive intervention for neurotypical elderly people or people with minor vascular cognitive disorders.
The aim is to find out whether AI techniques, and particularly customisation algorithms, can optimise the number of responders to an attention training programme.
Dementia is caused by a mixture of neurodegenerative lesions and cerebrovascular diseases (CVD) that include vascular lesions that are “hidden” but detectable with neuroimaging upstream from clinical events and are associated with increased stroke risk.
In France, it is estimated that more than 5 million people aged over 65 suffer from CVD and could benefit from attention training to prevent or delay strokes and major neurocognitive disorders such as dementia.
The project proposes for the first time to take up the challenge of customising attention training for elderly subjects using Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS), in a cognitive intervention clinical pilot study.
Health
ALOIS project 2023-2025
Therapeutic Education Programme
Early onset Alzheimer’s Disease affects 35,000 people in France. Given their age, no welfare structure is adapted to these patients requiring individualised psychosocial support. The project aims to create an innovative and multidisciplinary Therapeutic Education programme which would meet these patients’ specific needs in terms of behavioural disorders, and more particularly anxiety and stress management. The goal is to design and implement this programme in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region.
The project is being led by the Memory Research & Resources Centre team at Bordeaux University Hospital.
Due to their age, patients suffering from early onset Alzheimer’s face particular difficulties in managing the disease in a socioprofessional and family context. No welfare structure is adapted to their specific needs. In the early stages of the disease, these patients develop psychobehavioural disorders, particularly anxiety, which disable their daily life.
Given the lack of a Therapeutic Education programme in Nouvelle-Aquitaine, the idea behind this project is to create an innovative programme including modules on stress management through hypnosis and meditation. The programme will be built in 3 phases: design and training based on the analysis of young Alzheimer patients’ needs, implementation, and assessment with adjustment.
Once up and running, the aim is to continue this programme in the long term by incorporating it in the activities of the Memory Resource & Research Centre.
This project is led in partnership with the Pain and Integrative Medicine department of the Institute for Integrative and Complementary Medicine (IMIC) and the Transversal Therapeutic Education Unit of Bordeaux University Hospital.

Health
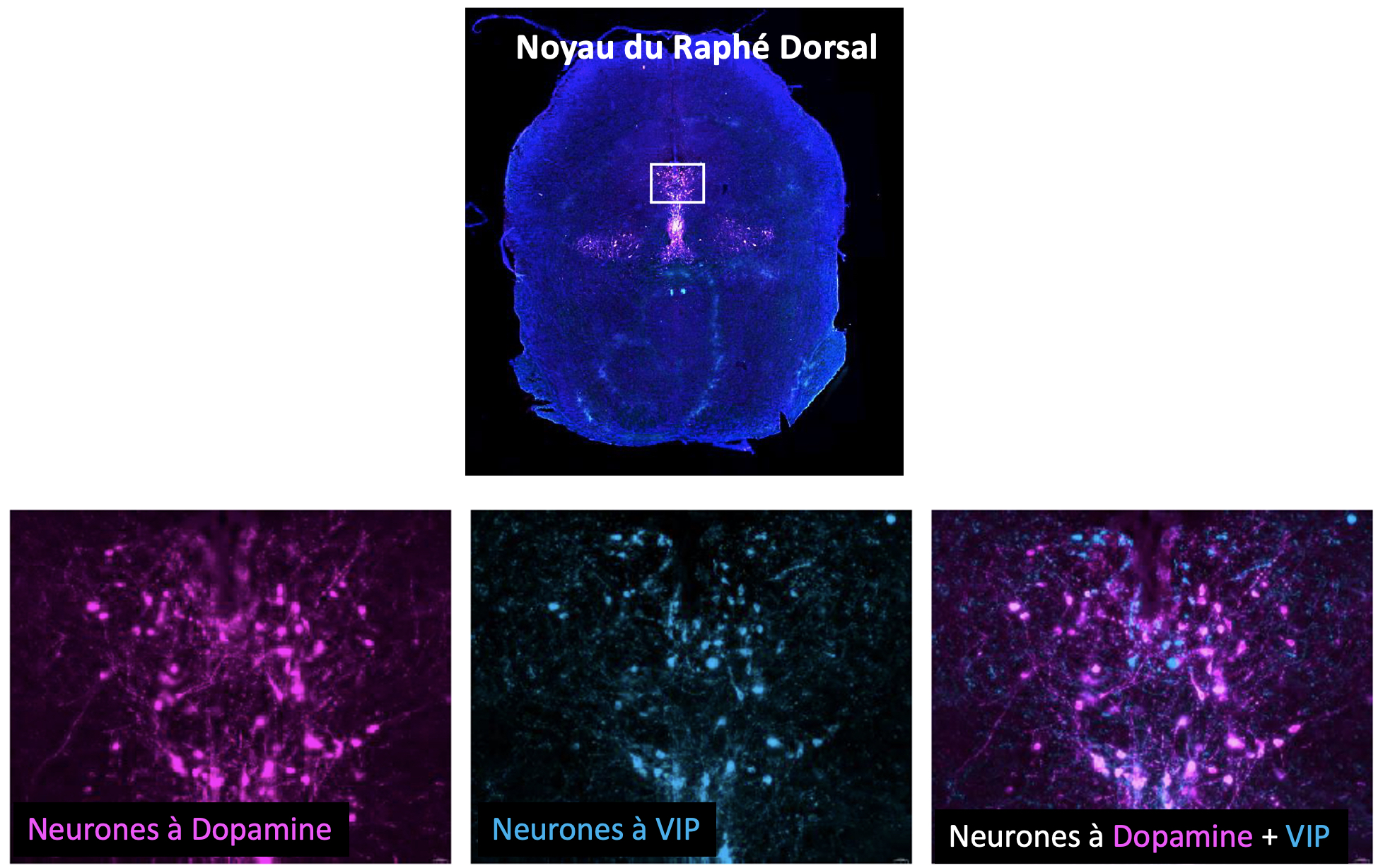
3rd Clément Fayat scholarship: VIP-PARK Medical research thesis 2023-2026
The aim of this thesis is to examine the dysfunction of one region of the brain and gain clearer insight into the neurological origin of anxiety, which has a considerable impact on the life of patients suffering from Parkinson’s Disease. The goal is to identify the effects of the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) produced by specific neurons on various brain structures and establish links between dysfunctional signals and the anxiety experienced by such patients, in order to improve their daily lives.
The research is being led by the Dopamine and Neuronal Assemblies team from the Institute for Neurodegenerative Diseases at Bordeaux University.
Parkinson’s is a neurodegenerative disease, characterised by its motor symptoms (trembling at rest, bradykinesis, stiffness, etc.), which affects several million people worldwide. The disease also has non-motor symptoms such as the anxiety which has a considerable impact on the life of Parkinson patients.
The dysfunction of a clearly-identified region of the brain, the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), would appear to be at the origin of the development of anxiety in patients. Highly-specific neurons associated with this region are notably capable of secreting a neuropeptide known as vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). This thesis thus aims to better understand the role and involvement of this neuronal population in the release of VIP, and subsequently find a new way to treat anxiety and improve life for Parkinson patients.
Health
The VERGER DES BALANS project
2023-2025
Therapeutic Education Programme
Alzheimer’s is the most common neurodegenerative disease. The Foundation supports the development of the Therapeutic Education Programme (TEP), at the GBNA clinic Le Verger des Balans in Dordogne, geared towards patients at a mild to moderate stage of Alzheimer’s or similar diseases, living at home with their caregivers.
The aim is to meet a growing demand from patients and caregivers to improve the quality of their daily lives.
This project is being led by the team from the Cognitive-Behavioural Unit of Le Verger des Balans (GNBA Santé), under the direction of ergotherapist Aurélie Jouhaud and psychologist Emma Poinot.
The development of Alzheimer’s and similar diseases has changed thanks to earlier diagnosis and adapted treatment. For patients suffering from mild effects, without loss of independence and living at home, therapeutic education is a way to meet the demand for care. Few programmes currently exist to this end in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region. In order to assist as many patients as possible, the Verger des Balans/GBNA Santé TEP has been organised so as to broaden its intake capacity. Structured around 6 workshops to provide patients and caregivers with knowledge and know-how, help them to manage their daily lives and plan new activities despite the disease, this programme is led by a team of specifically-trained experts. On completion of the workshops, an assessment is carried out on the quality of life and emotional load of patients and their caregivers.

Health
Project MUSIC-HD 2023-2025 Complementary non-pharmacological intervention
The Foundation is supporting a clinical trial of music therapy in combination with standard treatment for 15 patients with early-stage Huntington’s disease. This genetic neurodegenerative disease is characterised by movement disorders combined with psychiatric impairment in 35-75% of cases. This pilot study aims to evaluate whether music therapy reduces irritability, impulsivity and anxiety, and improves the quality of life of patients diagnosed with this illness in the early stages and their carers.
For this study, the MUSIC CARE © tool will be used, an innovative software program that brings patients into a state of relaxation using the “U sequence” method, which involves reducing the musical rhythm, orchestral formation, frequency and volume (descending U-shaped phase). :
The study will be undertaken at the Clinical Investigation Centre, CIC INSERM 1402 at Poitiers University Hospital, under the scientific responsibility of Dr Isabelle Benatru, hospital practitioner in neurology and head of the Parkinson’s Expert Centre and the Huntington’s Disease Competency Centre at Poitiers university hospital.

Health
TAP_DLB Project 2023 - 2025
Post-doctoral grant
Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is a neurodegenerative disease with no known treatment currently, caused by the pathological accumulation of a protein naturally present in the brain in its soluble form. This project's research involves analysing the brains of primates that have been injected with Lewy bodies extracted from the brains of deceased patients. This analysis is the final stage before a primate model of DLB can be developed, essential both to the understanding of this disease and the development of therapeutic solutions.
Research carried out by the Physiopathology of Proteinopathies team of the Neurodegenerative Diseases Institute of the Bordeaux university hospital, under the direction of Erwan Bezard, INSERM Research Director.
The research team has already performed a comparative study of primate brains with DLB, Parkinson's and multiple-system atrophy, which identified avenues for future research that are both common and specific to each of the three synucleinopathies (diseases characterised by the abnormal accumulation of synuclein proteins, a shared feature of these three illnesses). This study strengthens the possibility of offering multiple treatment strategies for DLB.
Download the publications:
npj_Parkinsons_Disease_DLB_2023.pdf Sci_Advances_NHP_2025_time_course.pdf
Health
VLHE_EVAL Project 2023 - 2024
Post-doctoral grant
Since being opened in June 2020, Village Landais Alzheimer (VLHE) has become home to approximately 110 people with Alzheimer's disease or a related illness. This experimental project, the only of its kind in France, is based on non-medication treatments and support tailored to the patient. The research study involves comparative analysis of economic data (program costs and use of treatments) and clinical data (cognitive and functional evolution) from village residents and residents in nursing homes. The objective is to evaluate and put into perspective the clinical efficacy and economic cost of each of the program's models, as well as the effects on healthcare professionals and carers.
This project is led by the PHARes team from Bordeaux Population Health, under the direction of Jérôme Wittwer, University Professor of Economics at the Bordeaux School of Public Health (ISPED).
The first dementia village was created in the Netherlands in 2009, with the concept then being launched in France by Henri Emmanuelli. The challenge of this project is to assess the effectiveness and overall cost of this innovative form of care using medico-economic analysis and to thereby provide information to public decision- makers who are considering establishing such.

Health
2nd Clément Fayat scholarship: COUNTER-PD
Medical research thesis 2022 - 2025
The aim of this thesis is to characterise the anatomical organisation of motor circuits in the brainstem and to restimulate them to restore movement for people with Parkinson's disease.
Work carried out by the Development and Neurobiology of Neural Networks team at the Institute for Cognitive and Integrative Neuroscience of Aquitaine.
Health
1st Clément Fayat scholarship: NAPAD
Medical research thesis 2021 - 2024
This thesis focuses on the use of intelligent nanovectors capable of targeting the lysosomes of specific nerve cells and restoring their function of cleaning up aggregated proteins whose accumulation contributes to the pathological mechanisms of Parkinson's disease.
Research carried out by the Physiopathology of Proteinopathies team at the Institute of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Download the publications:
NPJ Parkinsons Disease novembre 2025 Science Advance June 2025 NPJ Parkinsons Disease August 2024 Alzheimer's Dementia March 2024 BioConjugate Chemistry March 2023 Cells February 2023
Santé
CRI-AMS Project 2025-2026 Research Grant
This project aims to identify specific biomarkers associated with the severity of Multiple-system atrophy (MSA), a rare and progressive disease with no treatment to date. These biomarkers are a major issue for diagnosing patients accurately and at an early stage, in order to develop new treatments in therapeutic trials.
MSA is a rare, rapidly progressive neurodegenerative disease affecting a wide range of neurological functions. Today, there is no treatment that can modify its fatal evolution, which takes an average period of 6 to 10 years. It is responsible for severe motor impairment of motor skills and balance, and can affect swallowing as well as so-called autonomic functions, leading to urinary disorders and diseases associated with high blood pressure.
The diagnosis is based on essentially clinical criteria that lack precision. This leads to a delay in diagnosis, which is increasingly often four years after the onset of symptoms. Misdiagnoses are also commun, as the disease share many clinical similarities with other neurodegenerative diseases.
However, the prognosis of MSA is radically different from these other pathologies. This limitation is a significant obstacle to specialised care to prevent specific complications of the disease and to research new treatments in therapeutic trials.
Indeed, the effectiveness of current treatments and future clinical trials depends closely on identifying patients at early stages, i.e., before neuronal loss (which is irreversible) that leads to major sequelae.
The search for specific biological markers is therefore a major challenge in identifying patients accurately and at an early stage.
One of the main biological features of MSA is the presence of marked inflammation in the brain. This inflammation takes the form, for example, of an increased amount of molecules or cells involved in the immune response in the biological tissues of patients. It therefore represents a distinctive marker and a potential therapeutic target.
However, current studies are limited by small samples and restricted biological analyses. Based on the sample bank of the French MSA cohort, we propose to carry out a high-reliable and large-scale analysis (384 markers). Some preliminary results on a small sample of the cohort suggest that certain markers are associated with the pathology. With the help of this new collection, we hope to ultimately identify biological markers that will improve the diagnostic and prognostic accuracy of the disease.
This multidisciplinary project, led by David Bendetowicz, MD. PhD., of the Memory and Research Centre MSA team in the Neurology and Neurodegenerative Diseases Department at Bordeaux University Hospital, also involves Margherita Fabbri, MD. PhD. of the Memory and Research Centre MSA team of the Neurology Department of CHU Purpan Toulouse.
Health
PSP TPE Project 2024-2026 Therapeutic Education programme
This project aims to create the first national therapeutic education programme for progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) patients. PSP is a rare neurodegenerative disease that progressively affects mobility and causes with problems with balance, swallowing, speech and vision. This programme is an opportunity to maintain patients’ and carers’ quality of life.
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a rare and complex neurodegenerative disease characterised by motor, cognitive and behavioural disorders. At Angers University Hospital, the Memory Research and Resource Centre is a centre of expertise for rare forms of dementia, including PSP. There is currently no national therapeutic education (TPE) programme for this disease. However, its progression requires patients and their carers to develop coping skills. The development of a TPE programme provides a crucial opportunity for patients and their carers to maintain or even improve their quality of life with this incurable disease. This programme sets out to meet a number of essential needs :
- Patient autonomy – PSP leads to a progressive loss of autonomy. This programme will help patients develop a better understanding of their disease, recognise the symptoms and make decisions about their daily lives. Adapting their daily activities could slow their loss of autonomy and help them maintain the best possible quality of life.
- Support for carers – care givers play a crucial role in the treatment of patients. The programme will include a workshop dedicated to carers, which will provide them with tools and strategies for managing the disease on a daily basis and dealing with difficult behaviour. This will help to reduce carer burnout and improve the overall care environment.
- Multidisciplinary management – the complexity of PSP requires a multidisciplinary approach. Based on this principle, the programme will involve 14 PSP specialists from 10 different professions to ensure comprehensive and coherent treatment.
- Improved understanding of the care pathway – by actively involving patients in their care pathway, TPE addresses the progression of the disease and presents possible strategies for providing optimal support. A palliative care doctor who has been trained in TPE will also participate in the programme.
This programme, featuring seven group workshops, will be developed in partnership with the PSP France association. It will be proposed at various stages of the disease, but particularly at the time of diagnosis and when swallowing problems appear.
Link to the programme flyer
Training
Twelve Clément Fayat scholarships
Training at EATP Égletons 2025-2028
The Foundation has joined forces with EATP Égletons civil works training school to fund four scholarships a year over a three-year period for students enrolled on the “CAP” certificate of vocational aptitude for Equipment Operators, the “BAC PRO” vocational baccalaureate diploma in Civil Works and the “BAC PRO” Civil Works Equipment Maintenance training programmes.
By funding a personalised assistance scheme, the Foundation is helping to eliminate the obstacles to enrolment on these training programmes for young people with difficult personal circumstances.
The Clément Fayat Foundation provides a unique monitoring and customised skill upgrading programme and finances a specific scheme covering induction and mentoring for education and training.
This support opens up new opportunities to help young people with ambitious career plans overcome difficult personal circumstances. With EATP Égletons, the Clément Fayat Foundation offers them new prospects.

Health
AUMASMART project 2024 – 2027 Research grant
Over an 18-month period, the project aims to assess the link between progression in the autonomy of 100 patients with Alzheimer’s disease and progression of data on their daily smartphone use via use of an algorithm. The goal is to develop new non-invasive early markers to identify and track the progression of autonomy, in order to predict the progression of the disease and enable more customised treatment of patients.
In France, 1,200,000 people could be affected by Alzheimer’s disease or a similar disease. The first cognitive function affected is memory. Other cognitive systems are affected in the course of the progression of the disease, leading patients to gradually lose autonomy. Functional autonomy refers to patients’ ability to perform everyday tasks. The project starts from the hypothesis that there is a link between the progression of psycho-behavioural disorders, such as everyday smartphone use data, and the progression of the autonomy of affected patients.
The project aims to study links between the autonomy of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and smartphone use data, via the use of an algorithm, in order to identify predictive markers of autonomy and the appearance of psycho-behavioural disorders, with the aim of providing more customised treatment.
The development of an autonomy prediction tool will provide better information for both patients and their families on the progression of the disease, before the cognitive disorders become too severe, meaning they can play an active role in their disease regarding decisions on their health and express their wishes.
This multidisciplinary project, headed up by Adrien Julian, Doctor MD. PhD., from the DECLA team (functional DECLine and multimodal ANalysis) at the INSERM (French National Institute of Health and Medical Research) Clinical Investigation Centre 1402 at Poitiers University Hospital Centre, also involves the XLIM laboratory in Chasseneuil-du-Poitou, and the CerCA (Cognition and Learning Research Centre) laboratory at the University of Poitiers.

Training
Two Clément Fayat scholarships
2024-2026 Equipment Operation CAP vocational training course
The Clément Fayat Fondation is bolstering its partnership with EATP Égletons civil engineering school by funding two Clément Fayat scholarships for the 2024-2026 “Equipment Operation” CAP vocational training course.
This means obstacles to accessing the CAP equipment operation training course can be eliminated by sponsoring a customised bridging programme, providing individualised support.
One specific feature of Clément Fayat Foundation is how it provides monitoring and a customised bridging programme, by funding a specific educational and teaching support scheme.
This support opens up new possibilities for young people who want to advance with their project despite complicated personal situations. With EATP Égletons civil engineering school, Clément Fayat Foundation creates new opportunities.

Training
International Integration Grants
Training in machinery operation 2023
The goal of this project is to support young Ivorians from disadvantaged districts interested in public works professions, as part of a training-conversion programme in the Ivory Coast. In association with the École de la Deuxième Chance [‘The Second Chance School’], two applicants will thus be awarded the Clément Fayat international integration grant to follow training in machinery operation at the Egletons Vocational Training Centre for Public Works.
Each trainee will be supervised by a sponsor-mentor from Razel-Bec, and training will begin with a 2-week work placement, followed by seven weeks’ training at the Egletons Vocational Training Centre for Public Works.
This support forms part of the vast and ambitious Training-Integration project for young people seeking qualifications, in the framework of the overhaul of the Technical & Professional Education and Training scheme set up in the Ivory Coast.

Health
IPPLAMS Project 2023 - 2024
Post-doctoral grant
Using data from more than 692 French multiple-system atrophy (MSA) patients, the MSA rare disease reference centre of Bordeaux University Hospital and the biostatistics team of the Bordeaux Population Health Centre have modelled five evolving profiles of patients with different speeds of progression and mortality risks. The aim of the IPPLAMS project is to identify relevant biomarkers to establish a prognosis for this rare neurodegenerative disease, using these five scalable profiles.
Research carried out by team 12 of the Neurodegenerative Diseases Institute of Bordeaux University Hospital.
Biomarkers such as certain specific zones of cerebral atrophy or the concentration of neurofilaments in cerebrospinal fluid are likely to be significant.
Analysing the correlations between these five evolving profiles and targeted biomarkers should allow physicians to give patients prognostic information based on a brain MRI, a blood test and a lumbar puncture. The results will also make it possible to refine clinical trials for this rare disease.
This project is led by neurologist and doctor of epidemiology Alexandrea Foubert-Samier and her team, in partnership with Cécile Proust-Lima, doctor of biostatistics at INSERM, from the Biostat team at Bordeaux Population Health Centre.
MSA is a rare neurodegenerative disease with median survival of between six and ten years, for which there is no treatment to slow down the inevitable progression of the illness. Patients with MSA show a wide range in the progression of symptoms, representing a challenge in giving prognostic advice and an obstacle to developing neuroprotective treatment strategies.
Heritage
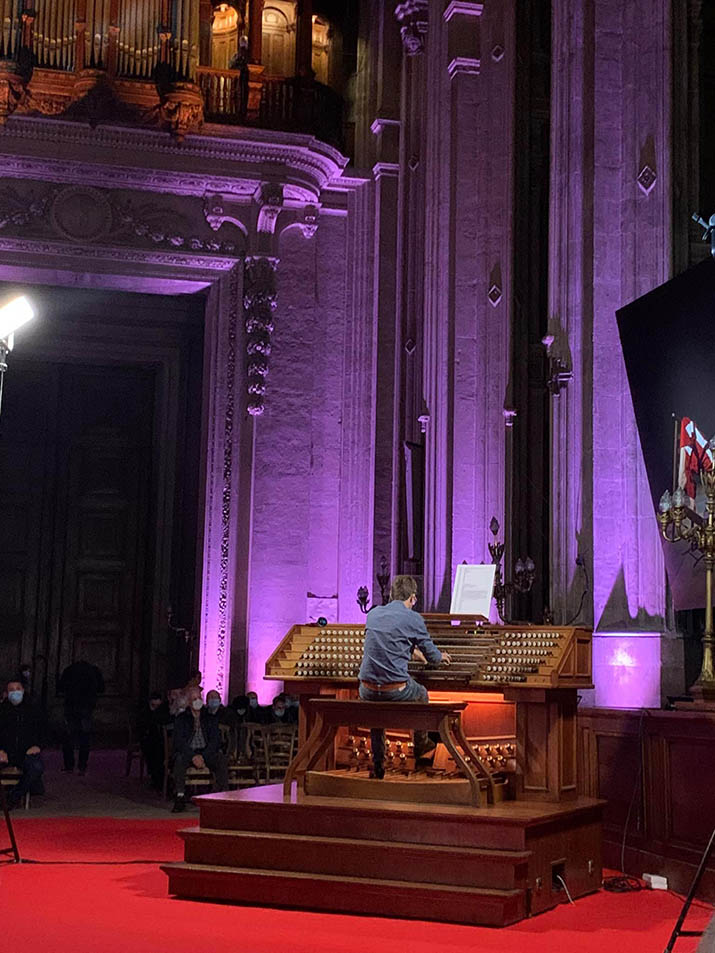
Raised mobile console for the pipe organ at Saint-André Cathedral in Bordeaux 2023 - 2026
The Clément Fayat Foundation is supporting the CATHEDRA Association in its high-quality reconstruction of the pipe organ, with funding for the creation of a raised mobile console. This innovation will allow the organist to play the pipe organ or the choir organ amidst the audience. As a private financial sponsor, the Foundation aims to revitalise the richness of French heritage and showcase the expertise of artisanal craftsmanship used in this stunning project.
The CATHEDRA Association is at the helm of this project, responsible for the development and promotion of the organs and religious music of the Bordeaux Cathedral.
This project has both heritage and cultural importance. It is essential to allow music to be played in the best conditions and to place Bordeaux back at the forefront of organ recitals, with unique repertoires and approaches to attract new audiences and young talents.

Heritage
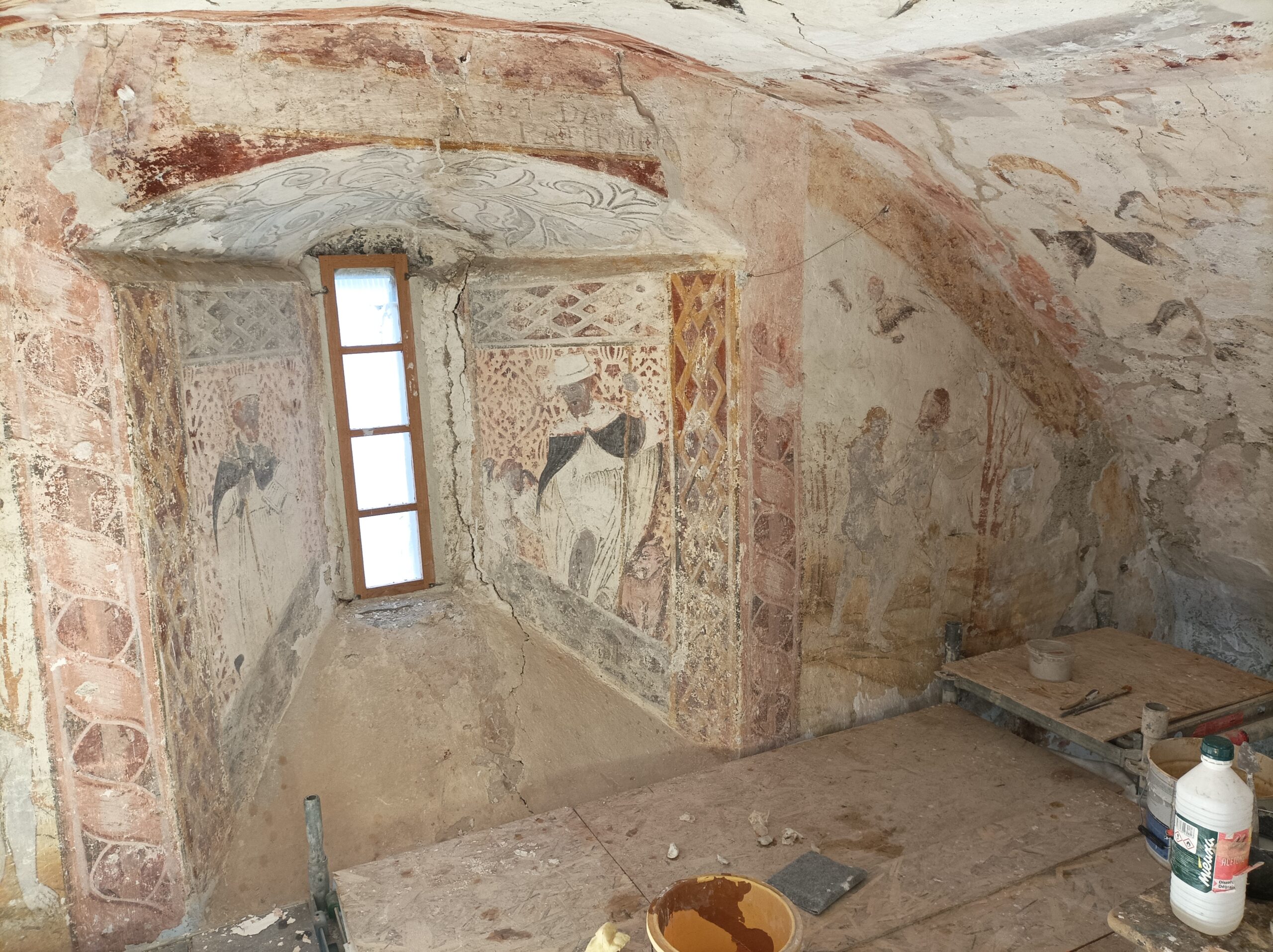
The Medieval wall paintings of Saint-Calixte Church 2025
The Foundation is supporting the uncovering of Medieval wall paintings hidden by centuries of whitewash. This project forms part of the Saint-Calixte restoration programme. The Roman church, a listed historical monument, is located in the mountainside hamlet of Cazaux-Fréchet, overlooking the Louron valley.
Saint-Calixte Church dates for the most part from the 11th century, with extensions dating from the 16th century. According to the legend, it was built in honour of the knight Saint-Calixte, who came to the aid of the valley’s inhabitants to fight the Moors in the 11th century.
The ensemble of outstanding wall paintings housed in this church testify to the continuity of worship over several centuries, with 11th-century Medieval style, 12th- and 15th-century Gothic, and other 16th-century works attributed to Melchior Rodiguis, a renowned figure of his time.
A team of experts is currently uncovering the first wall paintings. An unexpected number of fabulous masterpieces are starting to emerge.

Training
Two Clément Fayat Scholarships
Vocational training for machine operators 2023 - 2025
The aim is to offer two young people without a vocational training certificate the opportunity to enter the vocational training programme for machine operators, thanks to a pilot scheme to welcome them before the start of the school year and provide them with individual educational support.
This pilot project is structured around implementing a specific pedagogical framework:
Before the start of the new school year for the cohort, the scholarship recipients are introduced to the school and civil works occupations, and their academic level is assessed.
During the two-year course, they are mentored by two students from the years above and benefit from a specific academic support program supervised by teachers from general and vocational education.
The mentors and supervising teachers keep a journal tracking the students' progress.
An innovative project created in collaboration with EATP Égletons.

Heritage
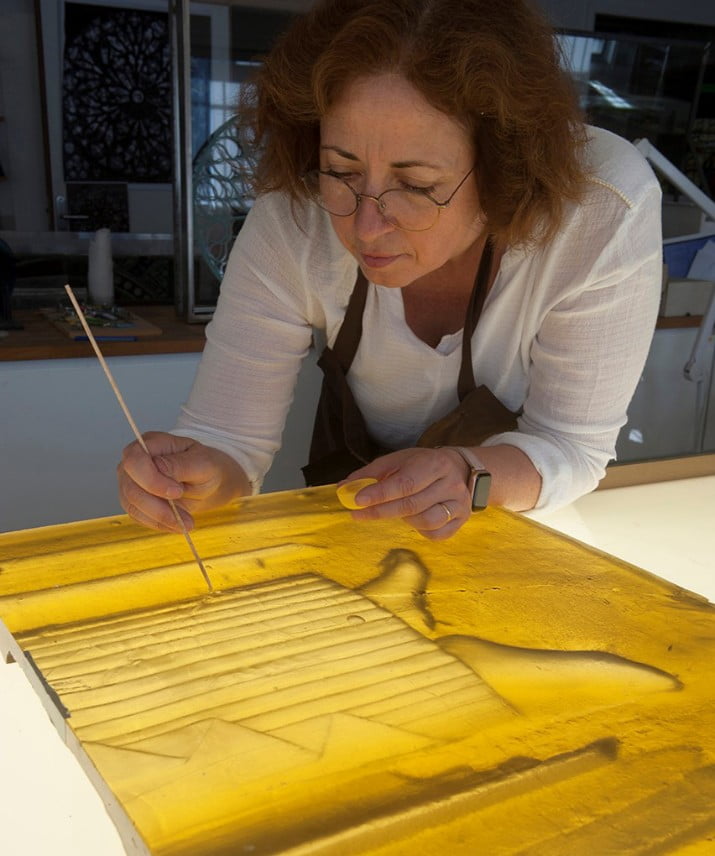
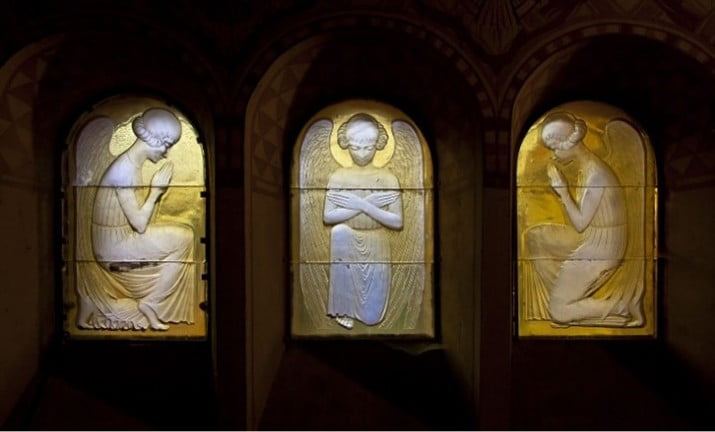
Lalique windows in Reims / 30 Angels by René Lalique in Saint-Nicaise Church 2022 - 2025
As a major founding sponsor, the Clément Fayat Foundation, alongside the Fondation du patrimoine, is contributing to the restoration of these 30 works of sacred art, which are exceptional both by their size and the technique used (moulded pressed glass). The windows are an example of the inventiveness and extraordinary creativity of master glassmaker René Lalique. The project to restore the church's glass windows is being carried out by the Association des Amis de Saint-Nicaise du Chemin-Vert.
The church was built in 1924, and was part of the innovative garden city project in Reims, by Georges Charbonneaux. It was designed to accommodate 600 large families of employees from Reims in single-family homes, including a vegetable garden and a henhouse.


Feedback

Heritage
Restoration of stained-glass windows created in 1926 by Renée Lalique Saint-Nicaise Church, Reims (51): 2022-2025 (Project Closed)
"For the restoration of 30 unique stained-glass windows crafted by the great master glassmaker, the support and commitment of the Clément Fayat Foundation—present since the project's launch in 2022— were decisive in ensuring its success. From April 2026, after three years of work, this beautiful edifice will once again be bathed in soft golden light, just as it was a century ago…"
Ghislain de Montgolfier
President of the Association « Les Amis de Saint-Nicaise du Chemin-Vert »

Research grant
Lewy Body Disease: 2023 - 2025 (Project Closed)
"Thanks to the support of the Clément Fayat Foundation, we were able to complete the development of the first preclinical primate model of Lewy Body Disease (LBD), a crucial missing link in validating therapeutic approaches before potentially moving into clinical trials (with patients). The specific characteristics of LBD will therefore be taken into account in therapeutic development."
Erwan BEZARD
INSERM – TAP_DLB Project Research Director

Therapeutic education
Programme for Progressive Supranuclear Palsy's patients: 2024-2026
"At Angers University Hospital, we offer a patient therapeutic education (PTE) programme dedicated to Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Thanks to support from the Clément Fayat Foundation, we have financed the training of two carers and acquired educational tools for our group workshops. We plan to create a promotional video to raise awareness of this programme at national level."
Cécile Authier
Nurse Coordinator Transversal Therapeutic Education Unit at Angers University Hospital ETP-PSP Project

Clément Fayat scholarship
Research thesis: 2021 - 2024 (Project Closed)
"Thanks to the Foundation's support in funding a doctoral thesis, we were able to advance our research project aimed at exploring new therapeutic research tracks for Parkinson's disease. The tangible results have reinforced the feasibility of this approach and encouraged further development of the research. Building on these successes, we are now considering extending the approach to other neurodegenerative diseases, with the goal of reaching more beneficiaries and ensuring a lasting impact, supported by regular progress monitoring."
Benjamin DEHAY
INSERM – NAPAD Project Research Director

Therapeutic education
Carers and patients programme Parkinson’s, early-onset Alzheimer's, Multiple Sclerosis: 2024-2026
"Numerous evidences suggest that mindfulness programmes are safe and effective for managing stress and psychological distress associated with neuro-evolutionary diseases in patients and their carers. Thanks to funding from the Clément Fayat Foundation, we will be able to create a digital platform to support these types of programmes within the framework of therapeutic education at Bordeaux University Hospital. We are grateful."
François Tison
Professor of Neurology

Research grant
Non-pharmacological intervention: 2024-2025
“Thanks to Clément Fayat Foundation’s support we will be able to advance the field of cognitive training for neurotypical ageing and pathology by providing “customised” training thanks to advances in Artificial Intelligence, responding to current issues relating to demographic ageing. This allows me to further my passion for and expertise with regard to ageing and technologies, opening up new possibilities.”
Marion Pech
Postdoctoral student - TOPAZ project

Research Grant
Multiple-system atrophy (MSA): 2023-2024
"The support of the Foundation has enabled significant progress in the knowledge of Multiples-system atrophy, a rare and particularly aggressive disease. Using sophisticated statistical models, groups of patients have been established, distinguished by the severity of their disease and their levels of biological markers related to neurodegeneration. These results open up new perspectives for patient monitoring."
David Bendetowicz
Postdoctoral Researcher IPPLAMS Project

Resarch grant
Village Landais Alzheimer (VLHE): 2023-2024
"I'm a doctoral student at the University of Bordeaux. My research evaluates the innovative Village Landais Henri Emmanuelli (VLHE) model for people with Alzheimer's disease. Over the last year, with support from the Clément Fayat Foundation, I have analysed the use of care by VLHE residents and demonstrated the concrete benefits of such a model. I would like to thank the Clément Fayat Foundation for its invaluable commitment to this innovative approach."
Damien Krier
Doctoral student-VLHE_EVAL project

Clément Fayat scholarship
Research thesis: 2024-2027
“I’m delighted to be able to continue my doctorate with a thesis in the field of neurosciences, which fascinates me, thanks to Clément Fayat Foundation‘s financial support. Fundamental research, whether focused on the brain or on other fields, is crucial to understanding our body. I am grateful that this funding is provided by a local foundation that actively supports research.”
Emma Perrot
Doctoral student-VIP-PARK project

Therapeutic education
Programme for young Alzheimer’s patients and their carers: 2024-2025
“The therapeutic education programme for young Alzheimer's patients and their carers was created with support from the Clément Fayat Foundation. This funding will also enable us to provide for the long-term future of the programme, which offers patients and their families practical tools to improve their quality of life with the disease. The feedback received has been very positive: the programme provides useful information and invaluable.”
Chloé Lazeras
Psychologist specialising in neuropsychology - ALOIS project

Clément Fayat scholarship
Research thesis: 2022-2025
"The support of the Foundation has enabled me to invest three years in this demanding project that I am passionate about: Exploring the contribution of a region of the brain to the regulation of our movements and the possibility of manipulating it to restore movement in Parkinson's disease."
"I would like to thank the Foundation's managers for the time they spent with the research team to understand the central issues of our experiments. Feeling supported makes me even more determined to make a significant contribution to this research project."
Abderrahman Fettah
PhD student - COUNTER-PD project

Clément Fayat scholarship
Research thesis: 2021-2024
“Support from the Foundation allows us to move forward with this ambitious project to explore new therapeutic avenues for Parkinson's disease using innovative technology, and helps fund my work in the laboratory. The interest shown by the Foundation's managers during their visits and their willingness to take the time to understand the details of the experiments shows a real commitment by the Foundation in this thesis, which motivates us to move forward with our research and make it accessible.”
Rémi Kinet
PhD student - NAPAD project



